Defined Benefit (DB) Plans
A type of pension plan in which an employer promises a specified pension payment and/or lump-sum upon retirement. The amount of the payment is typically derived from a combination of years of service, age, and compensation.
A traditional pension is a defined benefit plan.
Defined Contribution (DC) Plans
A type of retirement plan in which the employer, employee or both make contributions on a regular basis. The amount available at retirement depends on the amount contributed and the returns on the investments. The primary types of defined contribution plans explained below.
Common defined contribution plans include 401(k)s 403(b)s and 457 plans.
Defined Contribution (DC) Plan Types
-
401(k)s
For-profit institutions
Money grows tax deferred
Plans may offer a company match
Traditional and Roth options may be offered
10% penalty if distributed prior to age 59.5
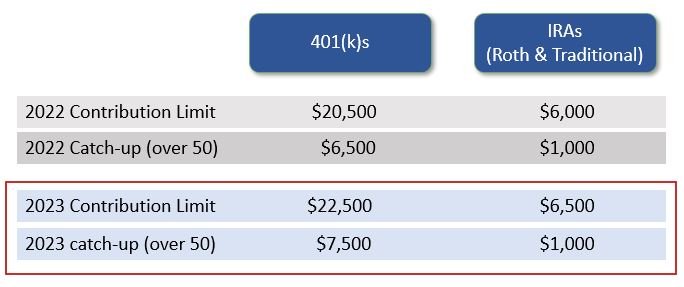
Annual Contribution limit (2023) = $22,500
-
403(b)s
Non-profit and government institutions
Plans may offer a match but not likely
Traditional and Roth options may be offered
10% penalty if distributed prior to age 59.5
Annual Contribution limit (2023) = $22,500
-
457
457(b) - for state and local government employees
457(f) - for non-profit executives
High contribution limits within three years of retirement
No penalty for distributions prior to age 59.5
Annual Contribution limit (2023) = $22,500
-
Thrift Savings Plan (TSP)
For federal employees and uniformed service personnel
Money grows tax deferred
Plans may offer a company match
Traditional and Roth options may be offered
10% penalty if distributed prior to age 59.5
Annual Contribution limit (2023) = $22,500
Retirement Plan Contribution Limits
IRAs
IRAs are not offered through an employer. Individuals may open an IRA through a financial institution.
Types of IRAs include traditional IRAs, Roth IRAs, SEP IRAs, and SIMPLE IRAs. Most people have a traditional or Roth IRA. SIMPLE IRAs are for companies with 100 employees or less and the SEP IRA can be opened by the self-employed.
Money held in an IRA usually can't be withdrawn before age 59½ without incurring a penalty of 10% of the withdrawal.
There are annual income limitations for deducting contributions to traditional IRAs and for contributing to Roth IRAs.
Contribution limits on IRAs are lower than those on defined contribution plans (currently $6,500 per year)
Social Security
A government run retirement benefit. Employees pay into social security through taxes that are taken out of their wages. At retirement age (currently no earlier than 62), employees can begin to receive benefits based on age, years of employment, and compensation.
Delaying social security can increase benefits.
Full retirement age is 66 (born prior to 1955), 67 (born 1955 or later)
People may elect to take benefits as early as 62, though benefits will be reduced.
Benefits can be delayed until age 70. There is no benefit delaying beyond age 70.
Non-Retirement Accounts
Many people save money outside of retirement accounts. This may include;
Brokerage accounts that allow the buying and selling of securities
Bank accounts
CDs
Real Estate investments
Life insurance policies
Annuities
For more information see saving and investing